We have a number of cancer patients training at our studios now with some amazing results. Particularly popular is our breast cancer rehab program. All of us have cancer in our body. Today more than ever we have a high plethora of cancer causing agents from the environment to our food supply. The only difference from a person diagnosed with cancer and those who don’t have cancer, is the immune system. For a number of reasons the immune system was not able to effectively police the cancer cells as fast as they divided.
Billions upon billions in cancer research and …………………
- In 1900 the risk of cancer was 1 person in 30
- In 1980 the risk of cancer was 1 person in 5
- In 1990 the risk of cancer was 1 person in 4
- In 1995 the risk of cancer was 1 person in 3
- in 2000 the risk of cancer was 1 person in 2
- Today the risk of cancer is even greater and continues to rise, in spite of medicine’s so called advances! Ref: Deepak Chopra, MD, Michael Murray, N.D, and the Metagenics group.
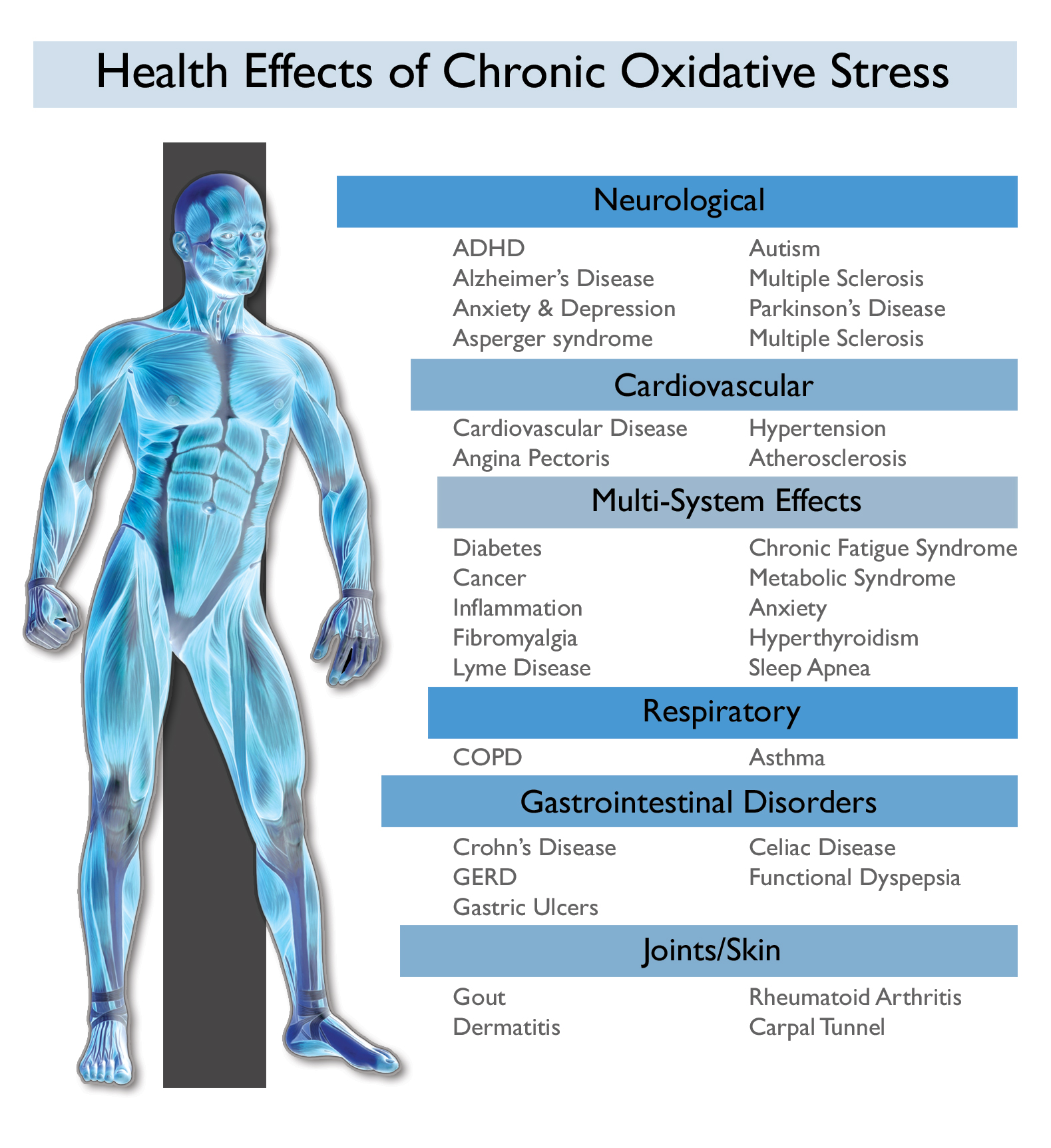 70-80% of the immune system is found in the digestive tract. Author of a new report in Clinical Reviews in Allergy and Immunology, Dr Natalia Shulzhenko, emphasises that our intestines contain more immune cells the entire rest of our bodies and that the human gut plays a “huge role in immune function”. According to Shulzenko an emerging theory of disease is that a disruption in the “crosstalk” between the microbes in the human gut and other cells involved in the immune system and metabolic processes.
70-80% of the immune system is found in the digestive tract. Author of a new report in Clinical Reviews in Allergy and Immunology, Dr Natalia Shulzhenko, emphasises that our intestines contain more immune cells the entire rest of our bodies and that the human gut plays a “huge role in immune function”. According to Shulzenko an emerging theory of disease is that a disruption in the “crosstalk” between the microbes in the human gut and other cells involved in the immune system and metabolic processes.
She adds that things like modern lifestyle, diet and overuse of antibiotics are causing an increasing disruption of the gut microbes that stimulate the immune system and that the chronic inflammation linked to most of the diseases that kill people in the developed world today may begin with dysfunctional gut microbiota.
1Keeping a delicate balance in the immune system by eliminating invading pathogens, while still maintaining self-tolerance to avoid autoimmunity, is critical for the body’s health. The gut microbiota that resides in the gastrointestinal tract provides essential health benefits to its host, particularly by regulating immune homeostasis. Moreover, it has recently become obvious that alterations of these gut microbial communities can cause immune dysregulation, leading to autoimmune disorders. Here we review the advances in our understanding of how the gut microbiota regulates innate and adaptive immune homeostasis, which in turn can affect the development of not only intestinal but also systemic autoimmune diseases.”
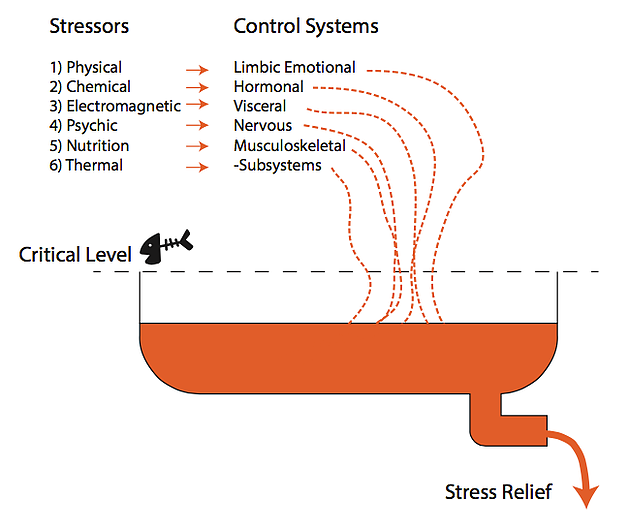
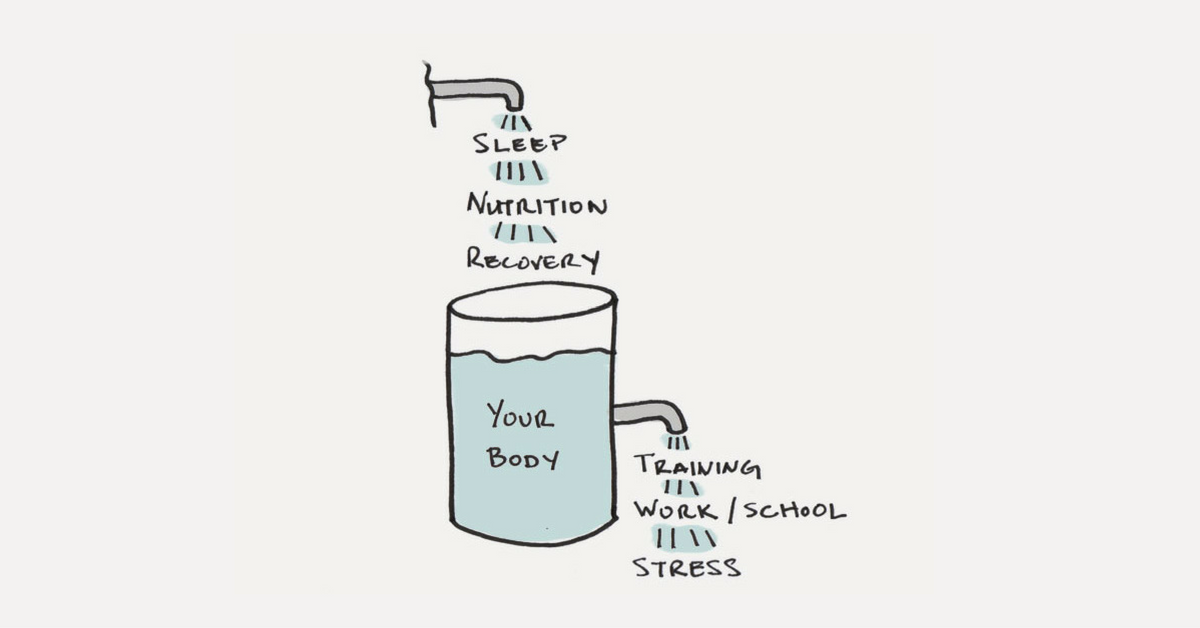
Today we are challenged by both physical and non physical stresses such as financial, nutritional, environmental, social or otherwise. We have to adapt to survive these stressors. The stresses are listed above in Paul Chek’s diagram. If the body cannot cope with amount of stress coming in the result is disease. To understand the stress-disease relationship response in the body, we need to consider the body as a bio -electric organism. All stress’s are interpreted as electric signals to the central nervous system. The body then summates these electrically interpreted stressors, providing an overall stress response that is unique to each individual.
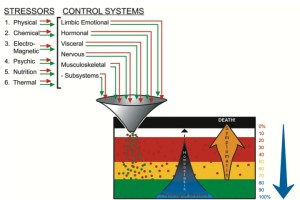
Now the body is considered a minimal electrical neuromuscular system(MENS), which means its functions best in an environment of minimum electrical stressors. this is born out of Arndt-Shultz law which states that weak stimuli activate physiological processes, moderate stimuli favour them and strong stimuli inhibit them.
Bibliography
‘Exercise for cancer patients’ – Paul Chek
1.The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity